Multi Beam Sputtering (MBS)
A new approach to ion beam sputter deposition
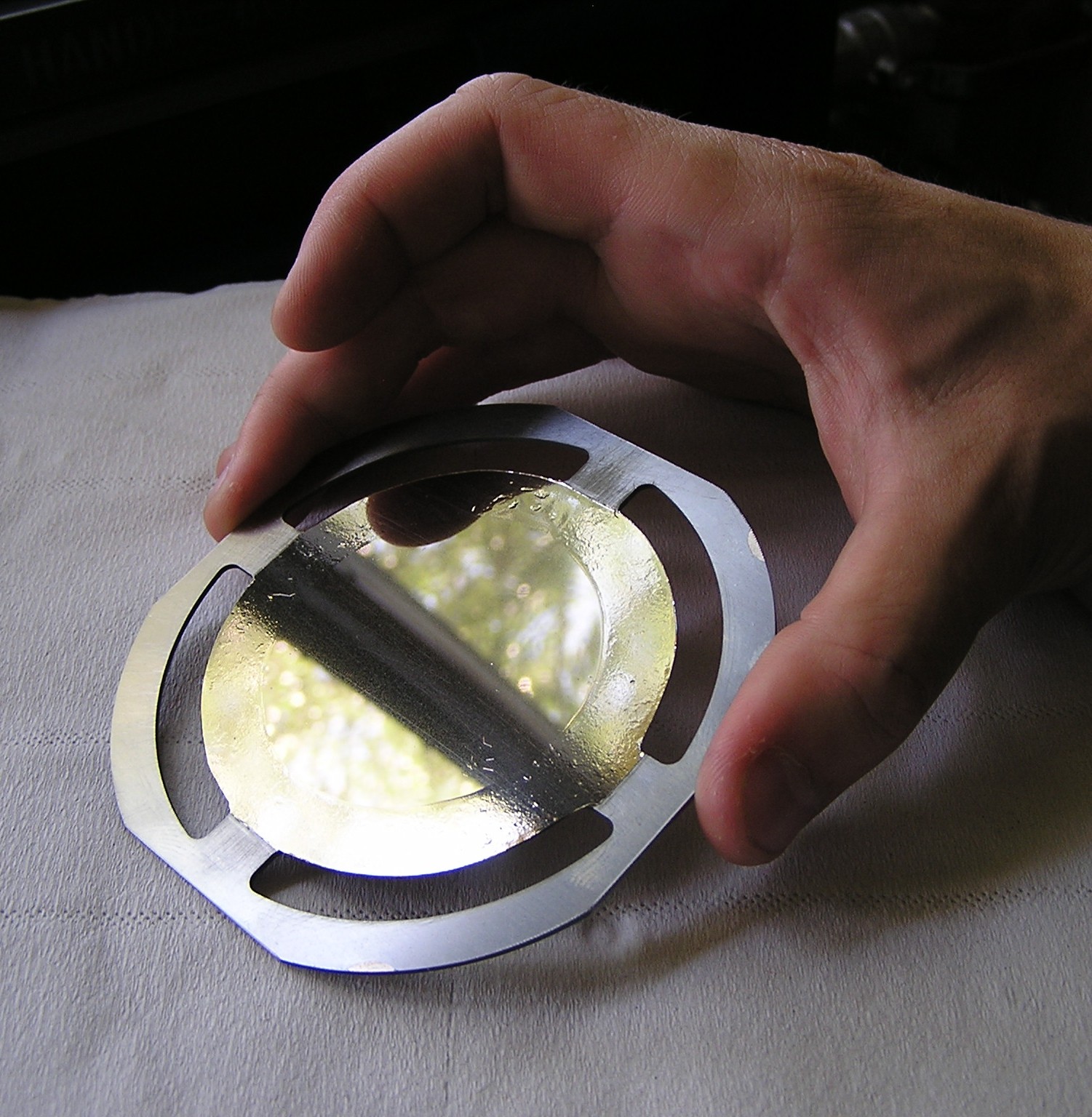
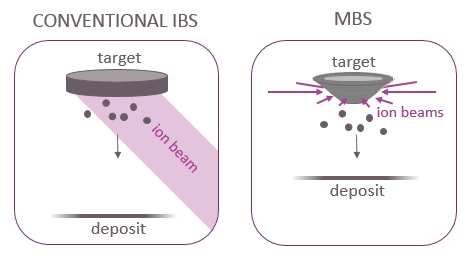
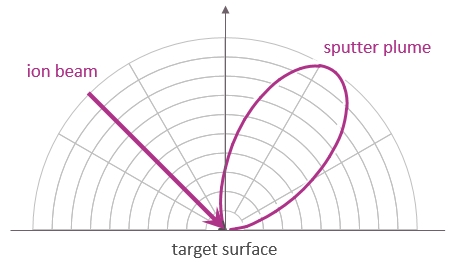
Conventional ion beam sputter deposition is done with a specific geometry: the sample is facing the target, and the ion beam is oriented at the target under an angle. The thickness of the deposit can be expected to be uniform over an area that is similar to the ion beam impact area on the target. The target itself needs to be a bit larger than the beam to avoid sputtering of the target holder.
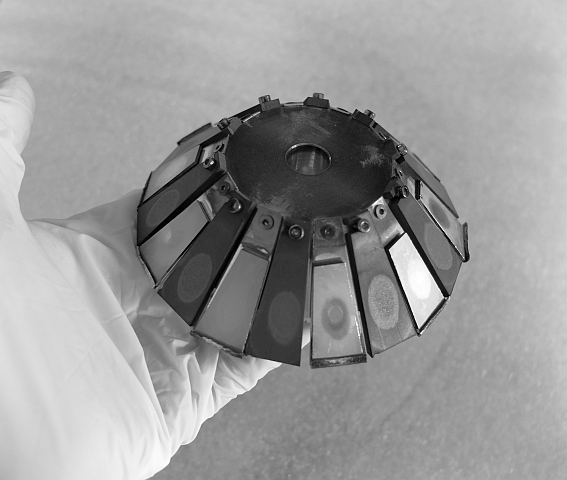
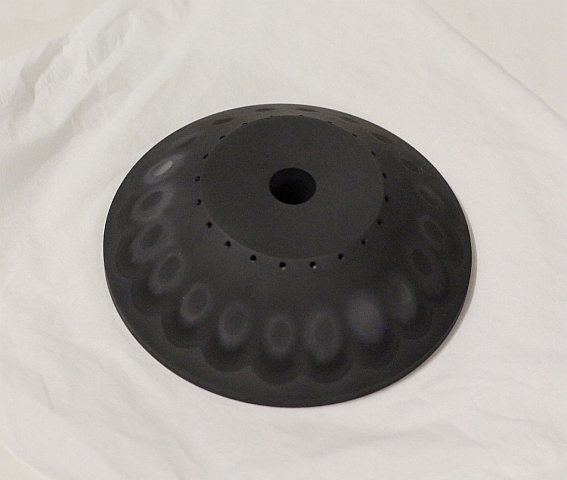


Full control over the deposition profile
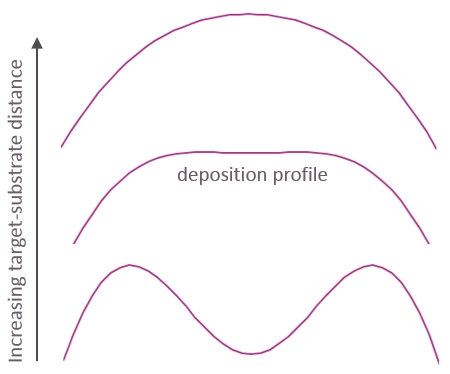
In a circular geometry with a conical target base, and equivalent ion beams, the thickness profile of the deposit will depend on the distance between the sample and the target. If the sample is very close to the target, the center of the sample will not receive any deposit. And if the sample is very far from the target, the film will be thickest in the center. At a sweet spot in between, the deposition profile displays a plateau for which the film thickness is uniform over an extended area. The position of that sweet spot depends on the size and shape of the used target base.
Multicomponent material deposition
Traditionally, deposition of thin films that consist of multiple elements is done either by using different targets for each element in a confocal geometry, or by using a single multi-element target. The latter is simpler, but less flexible, and has the drawback that the target composition will not remain constant over time due to different sputter rates for different elements. The confocal solution works well, but is less adapted to scaling to larger area depositions.
With multi beam sputter deposition it is possible to achieve multicomponent thin films with uniform composition based on mono-element targets in a geometry much more compact than a confocal one. Also, compared to other confocal deposition solutions, for a similar area with uniform deposition, the targets in MBS can be much smaller than in a confocal setup. Compared to confocal magnetron sputtering MBS offers an enormous flexibility in deposition parameters and feasible composition range.
Easy to operate
small footprint
modular and scalable
Multi-component thin films
Multi-layer thin films
Gradient thin films